From Side Hustle to Success Story
Ready to turn those fire Instagram shots into cold, hard cash?
Starting a photography business isn't just about having the latest camera gear or the perfect aesthetic feed anymore.
It's about building a legit empire that pays your bills, funds your travels, and lets you create art while making bank.
Whether you're tired of the 9-to-5 grind or just want to monetize your creative genius, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know to launch your photography business and actually make it profitable.
No cap "“ we're talking real business strategies, not just "follow your dreams" fluff.
Chapter 1: Finding Your Photography Niche and Market Research
Understanding Photography Business Types
Starting a photography business begins with identifying your specific niche in the vast photography market. The photography industry offers numerous opportunities, from wedding photography to commercial photography, each requiring different skills, equipment, and marketing approaches.
Popular Photography Business Niches:
- Wedding Photography: High-demand service with excellent profit margins
- Portrait Photography: Family portraits, senior pictures, headshots
- Event Photography: Corporate events, parties, celebrations
- Commercial Photography: Product photography, real estate, business marketing
- Fine Art Photography: Prints, galleries, online sales
- Stock Photography: Passive income through photo licensing
- Pet Photography: Growing niche with dedicated clientele
- Newborn Photography: Specialized skill with premium pricing
Market Research for Photography Business
Before launching your photography business, conduct thorough market research to understand your local photography market. Analyze competitor pricing, identify gaps in services, and determine your target audience's needs.
Research Steps:
- Study local photography businesses and their pricing structures
- Identify underserved photography niches in your area
- Survey potential clients about their photography needs
- Analyze seasonal trends in photography demand
- Research photography business licensing requirements in your state
Defining Your Target Audience
Successful photography businesses clearly define their ideal clients. Consider demographics, income levels, lifestyle preferences, and photography needs when identifying your target market.
Target Audience Factors:
- Age range and life stage
- Income level and spending habits
- Geographic location
- Photography style preferences
- Budget considerations
- Frequency of photography needs
Chapter 2: Essential Photography Equipment and Gear
Camera Equipment for Photography Business
Professional photography equipment forms the foundation of your photography business. While you don't need the most expensive gear to start, investing in reliable, quality equipment ensures consistent results and professional credibility.
Essential Camera Gear:
Primary Camera Body:
- Full-frame DSLR or mirrorless camera
- Backup camera body for redundancy
- Weather-sealed options for outdoor photography
- High ISO performance for low-light situations
Lens Collection:
- 24-70mm f/2.8 (versatile workhorse lens)
- 70-200mm f/2.8 (portrait and telephoto needs)
- 85mm f/1.4 (portrait photography)
- 35mm f/1.4 (wide-angle and environmental portraits)
- Macro lens for detail photography
Lighting Equipment:
- Speedlights and off-camera flash
- Softboxes and light modifiers
- Reflectors and diffusers
- Continuous lighting for video
- Light stands and mounting hardware
Photography Business Support Equipment
Beyond cameras and lenses, successful photography businesses require various support equipment for efficient operations and professional service delivery.
Technical Equipment:
- High-capacity memory cards and backup storage
- Professional tripods and stabilization gear
- External hard drives for data backup
- Color calibration tools for monitor accuracy
- Laptop computer for on-location editing
Business Operations Equipment:
- Professional camera bags and cases
- Business cards and marketing materials
- Contracts and legal documentation
- Payment processing systems
- Client management software
Equipment Investment Strategy
Starting a photography business requires significant equipment investment, but smart purchasing decisions can minimize initial costs while ensuring professional quality.
Cost-Effective Equipment Strategies:
- Buy quality used equipment from reputable sources
- Rent specialized equipment for specific projects
- Start with essential gear and expand gradually
- Consider equipment financing options
- Factor equipment costs into pricing structure
Chapter 3: Photography Business Legal Requirements and Setup
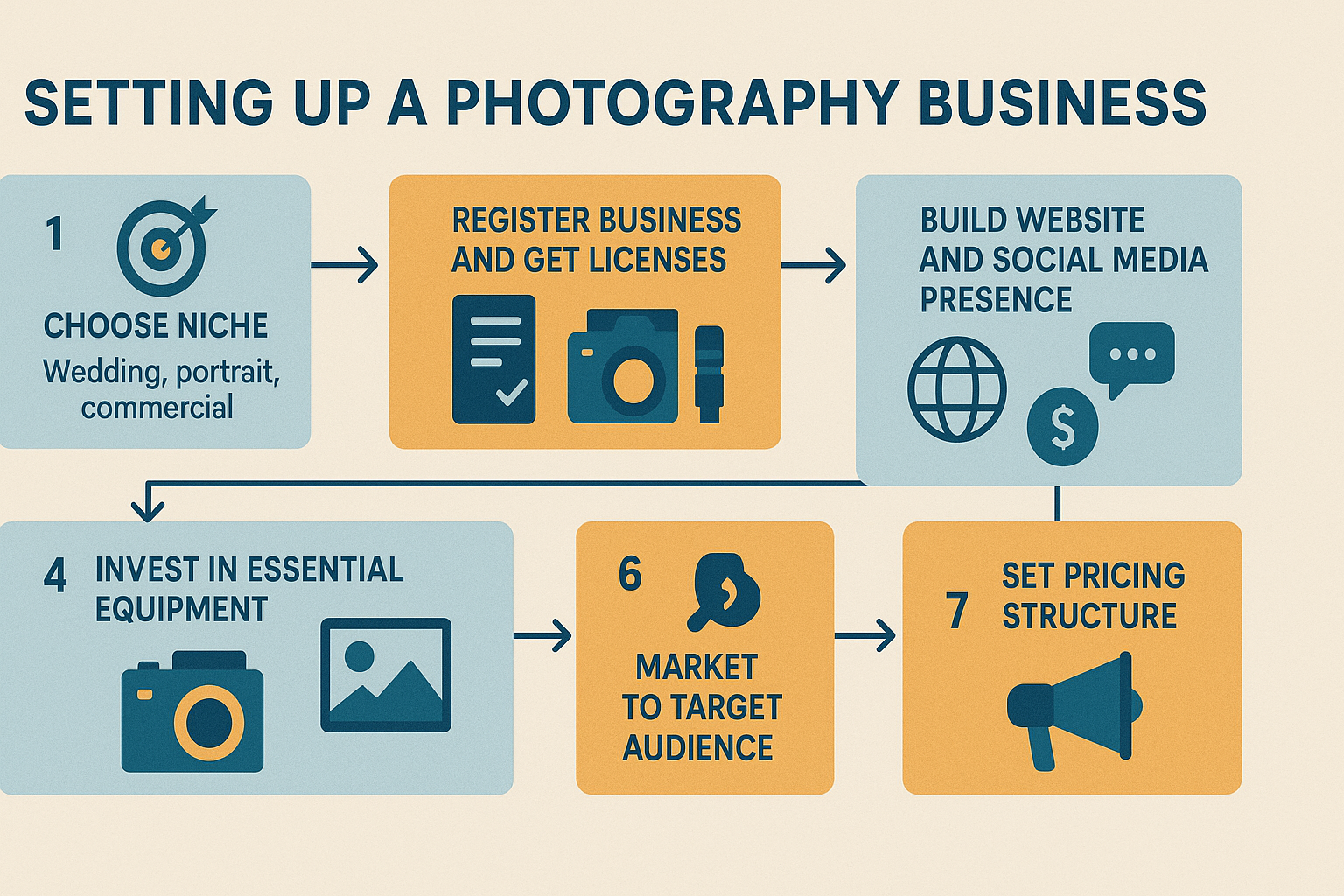
Business Structure and Registration
Establishing proper legal structure protects your photography business and personal assets while providing tax advantages and professional credibility.
Business Structure Options:
Sole Proprietorship:
- Simplest business structure
- Personal liability for business debts
- Direct tax implications
- Suitable for small photography operations
Limited Liability Company (LLC):
- Personal asset protection
- Flexible tax options
- Professional credibility
- Recommended for most photography businesses
Corporation (S-Corp or C-Corp):
- Maximum liability protection
- Complex tax implications
- Suitable for larger photography operations
- Consider professional consultation
Photography Business Licensing and Permits
Photography business licensing requirements vary by state and local jurisdiction. Research specific requirements in your operating area to ensure legal compliance.
Common Licensing Requirements:
- General business license
- Professional photography license (if required)
- Sales tax permit for product sales
- Occupational permits for studio operations
- Special event photography permits
Insurance for Photography Business
Professional insurance protects your photography business from various risks, including equipment damage, liability claims, and business interruption.
Essential Insurance Types:
Equipment Insurance:
- Covers camera gear theft and damage
- Includes off-premises coverage
- Consider replacement cost vs. actual cash value
- Factor in equipment depreciation
General Liability Insurance:
- Protects against third-party injury claims
- Covers property damage during photography sessions
- Essential for wedding and event photography
- Required by many venues
Professional Liability Insurance:
- Covers errors and omissions
- Protects against copyright infringement claims
- Includes failure to deliver contracted services
- Important for commercial photography
Photography Business Contracts and Legal Protection
Professional contracts protect your photography business interests and clearly define client expectations, payment terms, and service deliverables.
Essential Contract Elements:
- Detailed service descriptions
- Payment schedules and terms
- Image usage rights and licensing
- Cancellation and rescheduling policies
- Force majeure and liability limitations
Chapter 4: Photography Pricing Strategies and Profit Maximization
Understanding Photography Pricing Models
Successful photography businesses implement strategic pricing models that cover costs, generate profit, and reflect service value. Understanding different pricing approaches helps optimize revenue and client satisfaction.
Photography Pricing Models:
Hourly Rate Pricing:
- Simple calculation method
- Suitable for event photography
- Consider travel time and preparation
- Factor in post-processing time
Package Pricing:
- Bundled services and products
- Encourages higher client spending
- Simplifies client decision-making
- Popular for wedding photography
Session Fee Plus Products:
- Separate charges for photography session and prints
- Encourages additional sales
- Common in portrait photography
- Allows flexible pricing options
Value-Based Pricing:
- Pricing based on client value received
- Premium pricing for specialized services
- Reflects photographer expertise and reputation
- Suitable for luxury photography markets
Calculating Photography Business Costs

Accurate cost calculation ensures profitable pricing and sustainable business operations. Consider all business expenses when determining photography pricing structure.
Cost Categories:
Direct Costs:
- Equipment depreciation and maintenance
- Memory cards and storage media
- Travel expenses and mileage
- Assistant photographer fees
- Props and styling materials
Indirect Costs:
- Studio rent and utilities
- Insurance premiums
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Software subscriptions and licensing
- Professional development and education
Hidden Costs:
- Post-processing time
- Client communication and meetings
- Equipment backup and redundancy
- Business administration tasks
- Sick days and vacation time
Competitive Pricing Analysis
Understanding local photography market pricing helps position your photography business competitively while maintaining profitability.
Pricing Research Methods:
- Survey competitor websites and portfolios
- Analyze wedding venue preferred vendor pricing
- Research photography association price surveys
- Monitor social media pricing discussions
- Network with other photography professionals
Photography Product Sales and Revenue Streams
Diversifying revenue streams increases photography business profitability and reduces dependence on session fees alone.
Additional Revenue Opportunities:
- Print sales and wall art
- Digital image licensing
- Photography workshops and education
- Stock photography licensing
- Equipment rental services
- Photography tour leading
- Social media content creation
- Brand partnership collaborations
Chapter 5: Building Your Photography Portfolio and Brand
Creating a Professional Photography Portfolio
Your photography portfolio serves as the primary sales tool for your photography business, showcasing your skills, style, and professional capabilities to potential clients.
Portfolio Development Strategy:
Quality Over Quantity:
- Select 20-30 best images across different scenarios
- Maintain consistent editing style and quality
- Update portfolio regularly with recent work
- Remove weaker images as skills improve
Diverse Representation:
- Show variety within your chosen niche
- Include different lighting conditions
- Demonstrate technical proficiency
- Showcase personality and emotion
Professional Presentation:
- High-resolution images optimized for web
- Consistent watermarking and branding
- Logical organization and flow
- Mobile-optimized viewing experience
Photography Brand Development
Strong branding differentiates your photography business in a competitive market and attracts ideal clients who align with your style and values.
Brand Elements:
Visual Identity:
- Logo design and brand colors
- Typography and design consistency
- Photography style and editing approach
- Marketing material design language
Brand Voice and Messaging:
- Communication style and tone
- Value proposition and unique selling points
- Target audience messaging
- Social media personality
Brand Positioning:
- Market position (luxury, affordable, specialized)
- Competitive differentiation
- Service quality standards
- Client experience expectations
Photography Website Development
A professional website serves as your photography business headquarters, showcasing your work, communicating your brand, and converting visitors into clients.
Essential Website Elements:
Portfolio Galleries:
- Organized by photography niche or event type
- High-quality image optimization
- Fast loading times
- Mobile-responsive design
About Page:
- Personal story and photography journey
- Professional credentials and experience
- Client testimonials and reviews
- Contact information and availability
Service Information:
- Detailed service descriptions
- Pricing information or starting rates
- Booking process and timeline
- Frequently asked questions
SEO Optimization:
- Local search optimization for photography services
- Keyword-rich content and meta descriptions
- Google My Business profile optimization
- Client review management
Chapter 6: Photography Marketing and Client Acquisition
Digital Marketing for Photography Business
Effective digital marketing strategies help photography businesses reach target audiences, build brand awareness, and generate consistent client inquiries.
Social Media Marketing:
Instagram Marketing:
- Visual storytelling and behind-the-scenes content
- Hashtag research and strategic usage
- Instagram Stories and Reels engagement
- Influencer collaborations and partnerships
Facebook Marketing:
- Local community group participation
- Facebook Business Page optimization
- Targeted advertising campaigns
- Event promotion and marketing
TikTok Marketing:
- Short-form video content creation
- Photography tips and tutorials
- Trending audio and hashtag usage
- Authentic personality showcasing
Traditional Photography Marketing Methods
While digital marketing dominates modern business promotion, traditional marketing methods remain effective for local photography business growth.
Networking and Referrals:
- Wedding vendor networking events
- Local business association participation
- Client referral incentive programs
- Professional photographer association membership
Print Marketing:
- Business cards and brochures
- Local magazine advertising
- Direct mail campaigns
- Vendor fair participation
Client Relationship Management
Strong client relationships generate repeat business, referrals, and positive reviews that fuel photography business growth.
Client Experience Optimization:
- Professional communication throughout process
- Clear expectations and timeline management
- Timely delivery of final products
- Follow-up and relationship maintenance
Client Retention Strategies:
- Anniversary and milestone reminders
- Loyalty programs and repeat client discounts
- Seasonal promotion campaigns
- Personal relationship building
Photography Business Networking
Strategic networking builds valuable relationships that support photography business growth through referrals, collaborations, and industry insights.
Networking Opportunities:
- Wedding venue relationships
- Event planner partnerships
- Vendor collaboration networks
- Photography community participation
Chapter 7: Photography Business Operations and Workflow
Client Management Systems
Efficient client management streamlines photography business operations, improves client communication, and ensures professional service delivery.
CRM Software Features:
- Client contact information management
- Project timeline and milestone tracking
- Automated email communication sequences
- Invoice generation and payment processing
- Contract management and digital signatures
Popular Photography CRM Options:
- Pixieset (photography-specific features)
- Tave (comprehensive business management)
- Studio Ninja (all-in-one solution)
- HoneyBook (client experience focused)
- 17hats (small business management)
Photography Workflow Optimization
Streamlined workflows increase efficiency, reduce errors, and improve overall photography business profitability by minimizing time spent on administrative tasks.
Pre-Session Workflow:
- Client consultation and needs assessment
- Contract signing and deposit collection
- Session planning and location scouting
- Equipment preparation and backup checks
- Client communication and expectation setting
Post-Session Workflow:
- Image backup and organization
- Culling and selection process
- Post-processing and editing
- Client gallery creation and delivery
- Print fulfillment and final product delivery
Photography Business Financial Management
Proper financial management ensures photography business sustainability, tax compliance, and strategic growth planning.
Financial Tracking Systems:
- Separate business and personal accounts
- Expense tracking and categorization
- Invoice management and payment monitoring
- Tax preparation and quarterly payments
- Profit and loss analysis
Accounting Software Options:
- QuickBooks (comprehensive business accounting)
- FreshBooks (freelancer-friendly features)
- Wave (free small business accounting)
- Xero (cloud-based accounting platform)
- Excel or Google Sheets (manual tracking)
Equipment Maintenance and Backup Systems
Professional equipment maintenance and backup systems prevent business disruption and ensure consistent service quality.
Equipment Care Protocol:
- Regular cleaning and maintenance schedules
- Professional calibration and servicing
- Environmental protection and storage
- Insurance coverage and replacement planning
- Backup equipment availability
Data Backup Systems:
- Multiple backup location strategy
- Cloud storage and local backup combination
- Automated backup scheduling
- Client file retention policies
- Disaster recovery planning
Chapter 8: Photography Business Growth and Scaling
Expanding Photography Services
Strategic service expansion increases revenue opportunities and strengthens photography business market position.
Service Expansion Options:
- Additional photography niches
- Video production services
- Photo booth rental business
- Photography education and workshops
- Print and product fulfillment services
Team Building and Outsourcing
Growing photography businesses benefit from team expansion and strategic outsourcing to increase capacity and improve service quality.
Team Building Opportunities:
- Second shooter partnerships
- Photography assistant hiring
- Administrative support outsourcing
- Editing and post-processing teams
- Sales and marketing specialists
Photography Business Technology Integration
Modern technology solutions improve efficiency, enhance client experience, and support photography business growth.
Technology Solutions:
- Online gallery and proofing systems
- Automated workflow software
- Client communication platforms
- Social media management tools
- Online booking and scheduling systems
Market Expansion Strategies
Strategic market expansion increases photography business reach and revenue potential while diversifying client base.
Expansion Approaches:
- Geographic market expansion
- Target audience diversification
- Service offering enhancement
- Partnership and collaboration development
- Online market penetration
Chapter 9: Photography Business Financial Planning
Revenue Forecasting and Goal Setting
Successful photography businesses implement strategic financial planning to ensure sustainable growth and profitability.
Financial Planning Components:
- Annual revenue targets and milestones
- Monthly cash flow projections
- Seasonal demand fluctuation planning
- Equipment investment scheduling
- Business expansion funding requirements
Photography Business Investment Strategies
Smart investment decisions support photography business growth while maintaining financial stability and competitive advantage.
Investment Priorities:
- Essential equipment upgrades and replacements
- Marketing and advertising campaigns
- Professional development and education
- Business infrastructure improvements
- Technology and software solutions
Tax Planning for Photography Business
Proper tax planning minimizes photography business tax liability while ensuring compliance with federal and state requirements.
Tax Considerations:
- Business expense deduction optimization
- Equipment depreciation strategies
- Home office deduction eligibility
- Quarterly tax payment planning
- Professional tax consultation benefits
Photography Business Insurance Planning
Comprehensive insurance coverage protects photography business assets and ensures continuity during unexpected events.
Insurance Review Process:
- Annual coverage assessment and updates
- Equipment value appraisal and adjustment
- Liability coverage limit evaluation
- Deductible optimization strategies
- Multi-policy discount opportunities
Chapter 10: Advanced Photography Business Strategies
Photography Business Automation
Strategic automation reduces manual tasks, improves consistency, and allows focus on high-value photography business activities.
Automation Opportunities:
- Client inquiry response systems
- Social media posting schedules
- Invoice generation and payment reminders
- Gallery delivery notifications
- Follow-up communication sequences
Photography Brand Partnerships
Strategic brand partnerships create additional revenue streams and increase photography business visibility within target markets.
Partnership Types:
- Wedding venue preferred vendor programs
- Photography equipment brand ambassadorships
- Local business cross-promotion agreements
- Event planning company collaborations
- Social media influencer partnerships
Photography Business Metrics and Analytics
Data-driven decision making improves photography business performance and identifies growth opportunities.
Key Performance Indicators:
- Client acquisition cost and lifetime value
- Booking conversion rates
- Average transaction values
- Client satisfaction scores
- Social media engagement metrics
Photography Business Exit Strategies
Long-term planning includes consideration of photography business exit strategies and value maximization approaches.
Exit Strategy Options:
- Business sale to competitor or employee
- Franchise or licensing opportunities
- Passive income transition planning
- Asset liquidation strategies
- Succession planning development
Conclusion: Building Your Photography Empire
Starting a photography business requires careful planning, strategic investment, and consistent execution across multiple business areas. Success depends on combining technical photography skills with sound business practices, effective marketing strategies, and exceptional client service.
The photography industry offers tremendous opportunities for creative entrepreneurs willing to invest time and effort in building professional, profitable businesses. By following the strategies outlined in this guide, aspiring photography business owners can establish strong foundations for long-term success and sustainable growth.
Remember that photography business success doesn't happen overnight. Focus on continuous improvement, client satisfaction, and strategic growth to build a thriving photography business that supports your creative vision and financial goals.
Your photography journey starts now "“ take the first step toward building your photography empire today!
